
Structure hierarchy of proteins -Video-Watch Online
February 10, 2009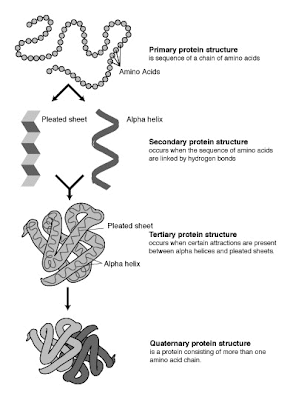
Protein structure-Video
Based on Structure hierarchy proteins are classified as primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structure.
- Primary Structure refers to the linear sequence of amino acids that make up the polypeptide chain.
- The secondary structure of protein molecules refers to the formation of a regular pattern of twists or kinks of the polypeptide chain. The regularity is due to hydrogen bonds forming between the atoms of the amino acid backbone of the polypeptide chain. The two most common types of secondary structure are called the alpha helix and ß pleated sheet.
- Tertiary structure refers to the three dimensional globular structure formed by bending and twisting of the polypeptide chain. This process often means that the linear sequence of amino acids is folded into a compact globular structure. The folding of the polypeptide chain is stabilized by multiple weak, noncovalent interactions.
- Quaternary structure refers that proteins contain more than one polypeptide chain. Each polypeptide chain in the protein is called a subunit. The subunits can be the same polypeptide chain or different ones.















