Top 10 Genome Annotation Tools of 2024: A Complete Guide for Gene Function Analysis
September 1, 202310 Best Gene/ Genome Annotation Tools & Software
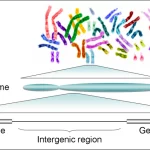
A process of identifying functional elements along a sequence of the genome that assigns a meaning to it is called genome annotation. This process is necessary because DNA produces sequences with both known and unknown functions.
In the past three decades, it has improved due to the computational annotation of protein coding genes on single genomes.
It is a multi-step process that is accomplished by the help of multiple tools based on genome analysis. In this article, we have highlighted the best gene and genome annotation tools for the purpose of gene function identification.
What Tools and Software are the Best for Gene and Genome Annotation?
Many complex steps are involved in this process, for which very sophisticated tools are needed. Hence, the best tools are handpicked by us based on their performance, availability, and citation in reputed published research.
We shall now describe the best gene and genome annotation tools and software used for every step in the next section.
Identification of RNA Genes
1. tRNAScanSE
tRNAScanSE is a de facto standard for the prediction of tRNA genes in entire genomes. It has incorporated advanced methodologies with probabilistic search software. Available on an online web server and also on a UNIX-based command line.
Widely accepted tool for the last two decades. The parameters for search options are several, such as sequence source, mode of search, type of query sequence (formatted/raw), output BED format, and more.
Some additional execution options are to disable peusdo gene checking, show the origin of first-pass hits, and show the primary and secondary structure components of scores. The choice of genetic code for tRNA isotype prediction is offered. Users can give a cutoff score.
KEY FEATURES
A widely adopted tool for finding tRNA genes in known/unknown sequences
A varied range of parameters are available to perform search
Standard output in the form of a list of genes in tabular format
Additional results can be generated using command line options
2. RNAmmer
RNAmmer is a genome annotation computational predictor’s tool for major rRNA species from different kingdoms of organisms. The program is based on a hidden Markov model that trains on the 5S ribosomal RNA database and the European ribosomal RNA database project.
A pre-screening step occurs in the tool that speeds up the process and loses very little sensitivity. It offers analysis of the complete bacterial genome within a minute of execution. On running RNAmmer on a large set of genomes, a very high level of accuracy can be expected.
Many genomes give results for novel and unannotated rRNAs. The tool is available on the CBS server along with the genome analysis results of some executed functions. Available for academic download when larger input files.
KEY FEATURES
Predicts 5s/8s, 16s/18s, and 23s/28s ribosomal RNA in full genome sequences
The input files are in fasta format for single or multiple sequences
Output format is GFF, also in XML, HMM, and FASTA
Parameters to choose kingdom: Archaea, bacteria, and eukaryotes
For Finding Genes/ORFs
3. Prodigal
Prodigal is a prokaryotic gene recognition and translation initiation site identification tool. It is based on the prokaryotic dynamic programming gene finding algorithm. It provides better gene structure prediction, improvements in translation initiation site recognition, and a reduction in false positives.
Data is fed on initiation codon usage (ATG vs. GTG vs. TTG), ribosomal binding site, motif usage, GC frame plot bias, and hexamer coding statistics for a complete training profile. It has a greater sensitivity for accurately identifying existing genes.
Used for the annotation of microbial genomes submitted to GeneBank. Also incorporated in the Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics microbial genomics browser. Valuable source for annotation of either drafts or finished sequences of microbes.
KEY FEATURES
A fast, lightweight and open source gene prediction program
The output consists of list of gene coordinates and protein translations
Detailed information about potential starts in the genome
Can be run into two steps: the training phase and prediction phase
Can be run in single step where training is hidden and final genes are obtained
4. GeneMark
GeneMark A combination of several gene prediction programmes developed at Georgia Institute of Technology, USA. An effective tool for prediction of genes in varied organisms such as prokaryotes, eukaryotes, viruses, phages, plasmids, and transcripts.
It is available for download and local installation. Based on the hidden Markov model and heuristic algorithms. It is part of the genome annotation pipelines at NCBI, JGI, Broad Institute.
Several tools are integrated in this package, such as QUAST, MetAMOS, MAKER2, BRAKER1, and BRAKER2. It is quite a popular and free bioinformatics tool used for different types of annotation functions.
KEY FEATURES
Available software package, QUAST for quality assessment of genome assemblies
MetAMOS for metagenomic assembly analysis
MAKER2 for eukaryotic genome annotation
BRAKER1 for RNA-seq based eukaryotic genome annotations
BRAKER2 for protein based eukaryotic genome annotation pipeline
5. MetageneAnnotator
Metagene Annotator is a comprehensive gene prediction tool that precisely predicts genes in prokaryotes from a single set of anonymous genomic sequences of different lengths. MGA has statistical models of prophage genes integrated into it, along with bacterial and archaeal genes.
Metagene Annotator can be downloaded on Linux and MacOS platforms. The input sequences should be less than 10 MBP in size for the web server. Only FASTA format sequences are taken as input.
It also takes self-training model from input sequences for predictions. The output includes the name of sequence, GC content in percentage, RBS, Gene ID, and the positions of detection. Widely accepted for microbial genome studies and genome annotations.
KEY FEATURES
Sensitive tool for detection of typical and atypical genes
Analyses Ribosomal Binding Sites RBS
Enables detection of a species specific patterns via RBS
Precisely predicts Translation starts of genes
Successful in improving prediction accuracy is for short sequences using RBS models
6. GrailEXP
GrailEXP is a Gene Recognition and Analysis Internet Link (GRAIL) that is popularly used systems for evaluation of the protein-coding potential of unknown DNA sequences.
Computational Biosciences dept at Oak Ridge National Laboratory employ it for the annotation of entire human genome. The tool also applies for microbial genome annotation and analysis.
The XGRAIL and genQuest are client-server applications used to locate exons on DNA sequences. Used to develop gene models and database search for homologs. Several parameters can be adjusted by the user before execution.
KEY FEATURES
Flexibility in input parameters- selection of organism, output format, searching database
Input DNA sequence either raw or fasta format
Output formats- Raw GrailEXP format, genome channel, human-readable text
Varied gene modeling organism choices available
Extended choice for Cpg Islands, Gawain gene models and repetitive elements
For BLAST Searches
7. GENBANK
GenBank is a database for genetic sequences, all annotated collection and publicly available data. GenBank is maintained by INSDC that includes DNA data from DDBJ, ENA, and GenBank at NCBI. Data exchange is very frequent among these organizations.
There are multiple ways to retrieve data from GenBank- Entrez Nucleotide for sequence identifiers and annotations. BLAST for local alignment sequence searches, NCBI e-utilities for downloading sequences and more.
The most updated and scientifically accurate data is available here. After finding ORFs/ genes, GenBank can be used to find similar sequences to the genetic region of the unknown organism.
KEY FEATURES
Comprehensively DNA data represented
Up-to-date and latest data available
Open source- free and public repository
Various operations- BLAST, deposition of data, retrieval done
Easy methods and multiple choices for searching data
8. UniProt
UniProt is an online facility for several tasks based on bioinformatics. It is maintained by EMBL-EBI the Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics and Protein Information Resource (PIR). A very comprehensive tool for protein sequence and annotation data.
External sources submit data to UniProt from where it is archived and revised. The UniProtKB is the protein knowledgebase that receives revised files from the archive.
In UniProtKB, automatically annotated data is generated by TrEMBL which is then exported to Swiss-Prot for review and manual annotation. The different repositories such as Proteomes constitutes the protein sets expressed by organisms and UniRef that has sequence clusters.
KEY FEATURES
Rich collection of annotated and reviewed data of protein and DNA sequences
Multiple sources send data to UniProt, data accuracy enhances
Heavily cross-referenced and connected to several sources
Open-source bioinformatics platform for public use
For Metabolic Pathways
9. KEGG database
KEGG database is a source for information based on high-level functions and utilities of biological systems- cells, organisms, and ecosystem, from genomic, molecular and chemical data. A computational representation for systems, with genes and proteins as building blocks.
Data is integrated with wiring diagrams of interaction, biochemical reactions, and relation networks. Disease and drugs information is present too. There are several categories of database for clear demarcations.
A very special feature called KEGG Orthology system is the basis for genome annotation and mapping. Organism specific pathways (metabolic reconstruction) is feasible. Using EC number, automatic matching of terms with the organisms can be done.
KEY FEATURES
Encyclopaedia for information on genes and genomes
Clear cut representation of biological relations using intriguing diagrams
Diseases and drugs study is very smooth
Annotated information for every organism
Integrated with several outside sources
For Protein Domain Search
10. InterProScan
InterProScan is an annotation source that provides information on functional analysis of protein sequences by classification into families. It predicts protein domains and important sites.
Open source with key values of heavy integration with diagnostic tool. Rich functional annotation and addition of relevant GO terms for automatic annotation of million GO terms across protein databases.
It uses predictive models called signatures (provided by member databases) that form the consortium. Incudes database- CATH, HAMAP, CDD, SMART, SFLD, SUPERFAMILY, TIGRfams, Prosite, PRINTS, Pfam, Panther, MobiDB Lite, and PIRSF.
KEY FEATURES
Updated every two months, latest information available
Open source and free to use by science community
Intuitive website for easy navigation by beginners
Results can be obtained regarding protein families, domains and sites
Sequence search or InterPro annotations browsing is offered
Annotation is not a single step process, hence each executions must be carried out cautiously to avoid false positives at the end. In this article, we have categorically mentioned the best gene and genome annotation tools at different steps in the whole annotation process.
You may go for these free genome annotation tools to obtain best results in research. Each of them is expected to produce precise, accurate and sensitive data.